What is the story about?
What's Happening?
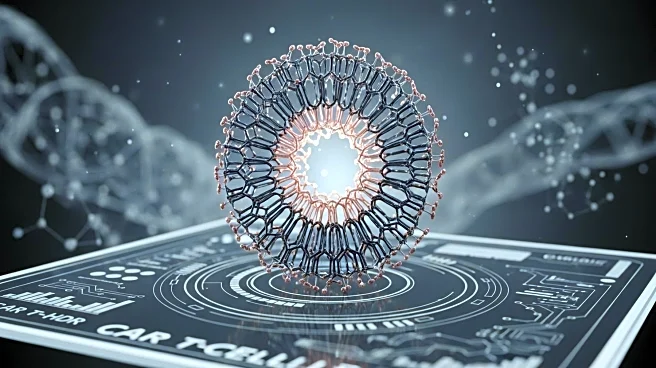
Recent advancements in CAR T-cell therapy have significantly improved cancer treatment, particularly for hematologic cancers. The therapy involves equipping T cells with synthetic receptors to target tumor antigens, such as CD19 in B cell malignancies, allowing for precise cancer cell destruction. Despite these advancements, challenges like antigen loss and limited success in solid tumors persist. To address these, researchers have employed the Proximity Network Assay to investigate the membrane architecture of CD19-targeting CAR T cells. This high-multiplex, sequencing-based assay maps protein organization at single-cell resolution, providing a detailed view of immune receptor organization. The study revealed significant insights into the spatial organization of CAR molecules and their interaction with other proteins, which could guide the optimization of CAR T-cell activity.
Why It's Important?
The findings from the Proximity Network Assay are crucial for enhancing the therapeutic potential of CAR T-cell therapies. By understanding the spatial organization of CAR molecules and their interactions, researchers can develop strategies to overcome current limitations, such as antigen loss and T-cell dysfunction. This could lead to more effective treatments for a broader range of cancers, including solid tumors. The ability to map protein interactions at a single-cell level also opens new avenues for personalized medicine, allowing for tailored treatments based on individual cellular profiles. This advancement could significantly impact the biotechnology and healthcare industries by improving the efficacy and scope of cancer immunotherapies.
What's Next?
Future research will likely focus on further refining the Proximity Network Assay to enhance its resolution and applicability across different CAR T-cell constructs. Researchers may also explore the assay's potential in other areas of immunotherapy, such as checkpoint inhibitors and bispecific antibodies. Additionally, clinical trials could be designed to test the efficacy of CAR T-cells optimized using insights from the assay, potentially leading to new treatment protocols. Stakeholders in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may invest in developing similar assays to improve other therapeutic modalities.
Beyond the Headlines
The use of the Proximity Network Assay highlights the growing importance of spatial proteomics in understanding complex biological systems. This approach could revolutionize how researchers study cellular interactions and signaling pathways, leading to breakthroughs in various fields beyond oncology. Ethical considerations may arise regarding the accessibility and cost of such advanced technologies, emphasizing the need for equitable distribution of healthcare innovations.