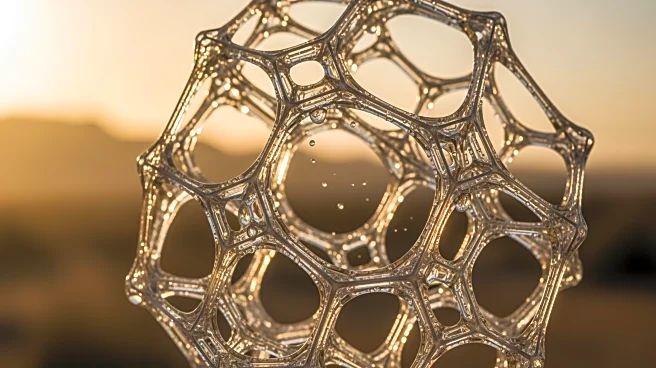
What's Happening?
Recent advancements in metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have significantly improved the efficiency of atmospheric water harvesting, particularly in arid regions with low humidity. These materials, recognized
for their superior water uptake and release properties, have demonstrated practical viability in desert environments. MOFs are hybrid materials composed of metal ions and organic linkers, forming highly porous networks that allow for precise design and interaction with different molecules. Beyond water harvesting, MOFs are effective in water purification, capable of selective adsorption of contaminants and degradation of pollutants. The commercial advancement of MOFs has gained momentum, with pilot systems engineered by Omar Yaghi’s research group showcasing MOF-based atmospheric water harvesting using solar energy.
Why It's Important?
The development of MOFs represents a significant breakthrough in addressing water scarcity in arid regions, offering a low-energy alternative for extracting water from the atmosphere. This technology has the potential to transform water management practices, particularly in areas facing severe drought conditions. By providing efficient water capture and purification solutions, MOFs can enhance water security and support sustainable development in regions with limited freshwater resources. The integration of MOFs into functional devices and the scaling up of their synthesis could lead to widespread adoption, reducing reliance on traditional, energy-intensive water extraction methods.
What's Next?
Further research and development are needed to overcome challenges such as the high production costs and potential degradation of MOFs over time. Efforts are underway to create more water-stable MOF structures and environmentally friendly synthesis techniques. Comprehensive life cycle assessments and environmental impact studies are essential to ensure the sustainability of MOFs and guide their responsible integration into water-related technologies. As the technology matures, it may become a key component in global strategies to combat water scarcity and improve access to clean water.
Beyond the Headlines
The use of MOFs in water harvesting and purification could have broader implications for environmental remediation and resource recovery. Their ability to selectively interact with different molecules makes them suitable for applications beyond water-related technologies, such as gas separation and pollution remediation. The versatility of MOFs could lead to innovative solutions across various sectors, addressing both environmental and resource recovery challenges. As interdisciplinary collaboration continues, the role of MOFs in water-related technologies is expected to grow, potentially reshaping the landscape of water management and environmental sustainability.