What is the story about?
What's Happening?
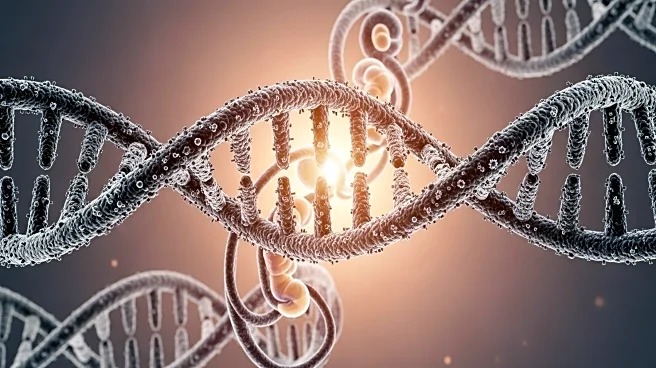
Researchers at Stanford University, led by biologist Raquel Fueyo, have uncovered a significant role played by remnants of ancient viral DNA in human embryonic development. The study, published in Nature, reveals that these viral DNA fragments, specifically a group known as LTR5Hs, are crucial for the proper formation of the blastocyst, a key early stage in embryonic development. The team used a 3D model of stem cells, called a blastoid, to mimic this stage. They found that disabling LTR5Hs resulted in disorganized cell growth or cell death, indicating the gene's essential role in forming the epiblast, a critical tissue layer. The research highlights how these viral remnants, which constitute up to 9% of human DNA, have been integrated into our genome over millions of years, providing evolutionary advantages by enhancing the expression of genes like ZNF729, crucial for stem cell multiplication and identity.
Why It's Important?
This discovery sheds light on the complex interplay between ancient viral DNA and human evolution, emphasizing how these remnants have been repurposed to support essential biological functions. The findings could have profound implications for understanding human development and genetic diseases. By revealing the role of LTR5Hs in embryonic development, the research opens new avenues for studying genetic disorders linked to early developmental stages. It also underscores the evolutionary significance of viral DNA in shaping human biology, potentially influencing future genetic research and therapeutic strategies.
What's Next?
The study's findings may prompt further research into the role of other viral DNA remnants in human biology and their potential links to genetic disorders. Scientists might explore how these elements can be manipulated for therapeutic purposes, particularly in regenerative medicine and developmental biology. Additionally, the research could lead to a deeper understanding of the evolutionary processes that have shaped the human genome, offering insights into the genetic basis of human uniqueness and adaptability.
Beyond the Headlines
The integration of viral DNA into the human genome raises intriguing questions about the ethical and evolutionary implications of genetic research. As scientists continue to uncover the roles of these ancient elements, there may be debates about the potential for genetic manipulation and its impact on human evolution. The study also highlights the interconnectedness of life, illustrating how ancient viral infections have contributed to the complexity of human development and evolution.