What's Happening?
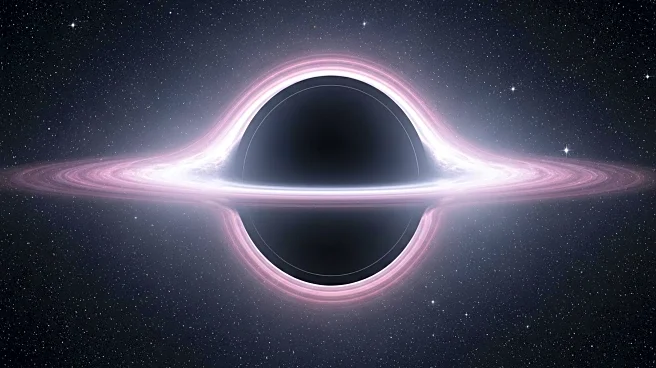
Astronomers using data from the James Webb Space Telescope have identified what may be the oldest black hole in the universe, potentially formed less than a second after the Big Bang. This discovery, detailed in a study awaiting peer review, could provide significant evidence for the existence of primordial black holes, a concept that has been debated among scientists for decades. These black holes are thought to have formed in the universe's earliest moments, challenging the traditional understanding that black holes originate from the collapse of massive stars. The findings suggest that this black hole, located in a region with minimal surrounding galaxy material, could be a primordial black hole, offering new insights into the universe's evolution.
Why It's Important?
The potential discovery of a primordial black hole has profound implications for our understanding of the universe's formation and evolution. If confirmed, it could reshape theories about how black holes form and grow, particularly those that are ancient and massive. This discovery also opens up the possibility that primordial black holes could be candidates for dark matter, a mysterious substance that makes up a significant portion of the universe's mass. The identification of such black holes could provide a new avenue for understanding dark matter and its role in cosmic evolution, impacting fields ranging from astrophysics to cosmology.
What's Next?
Further research and observations are needed to confirm the nature of this black hole and its primordial status. The study's authors suggest that future advancements in gravitational wave detectors could provide more definitive evidence. As the debate continues, astronomers will likely focus on gathering more data to support or refute the primordial black hole hypothesis. This ongoing research could lead to a paradigm shift in how scientists understand the early universe and the formation of its most enigmatic objects.
Beyond the Headlines
The discovery of a potential primordial black hole raises questions about the conditions of the early universe and the processes that led to the formation of such objects. It challenges existing cosmological models and suggests that the universe's initial conditions may have been more complex than previously thought. This could lead to new theoretical models and simulations to better understand the universe's infancy and the role of black holes in cosmic history.