What is the story about?
What's Happening?
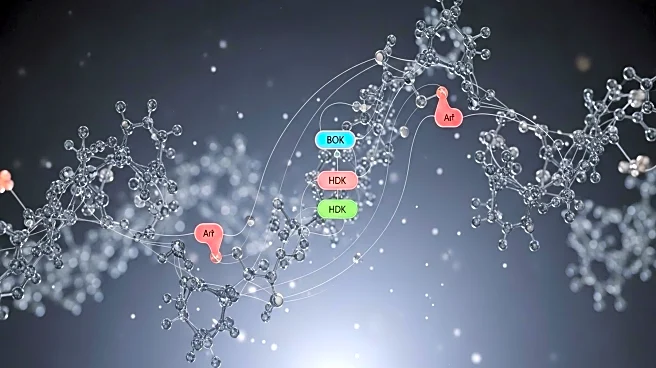
Researchers at the University of Washington have made significant advancements in targeted drug delivery through the development of Boolean logic-programmed proteins. Led by Cole DeForest, PhD, the team has engineered proteins capable of performing complex logical operations based on biological cues, such as AND, OR, and YES gates. These proteins, equipped with self-folding tails, can autonomously control drug localization and release, responding to specific environmental conditions like enzyme presence or pH levels. This innovation allows for precise targeting of therapeutic cargo within the body, potentially minimizing off-target effects. The study, published in Nature Chemical Biology, highlights the scalability of this approach, with living cells used as factories to produce these complex proteins efficiently.
Why It's Important?
The development of Boolean logic-programmed proteins represents a breakthrough in precision medicine, offering the potential to enhance the efficacy and safety of drug delivery systems. By enabling proteins to act as autonomous decision-makers, this technology could significantly reduce the risk of side effects associated with conventional treatments that affect healthy tissues. The ability to target specific disease tissues with high precision could revolutionize treatment protocols for various conditions, including cancer. Furthermore, the scalability of this approach, as demonstrated by the researchers, suggests that it could be applied widely, potentially transforming the pharmaceutical industry and improving patient outcomes.
What's Next?
The research team at the University of Washington plans to explore further applications of this technology, including its use in diagnostic tools and the manufacture of therapeutic proteins within individual cells. The potential to create larger logical circuits responsive to multiple biomarkers opens new avenues for complex treatment strategies. As the technology continues to advance, it may lead to the development of more sophisticated therapies that can be tailored to individual patients, enhancing personalized medicine. The researchers are optimistic about the future possibilities, aiming to refine the technology for broader clinical applications.
Beyond the Headlines
The ethical implications of this technology are significant, as it raises questions about the control and regulation of autonomous biological systems. Ensuring the safety and efficacy of these programmable proteins will be crucial as they move towards clinical trials and potential commercialization. Additionally, the ability to target specific cells within the body could lead to advancements in gene therapy and regenerative medicine, offering hope for treating previously incurable diseases. The long-term impact on healthcare systems and patient care could be profound, necessitating careful consideration of the societal and ethical dimensions.