What's Happening?
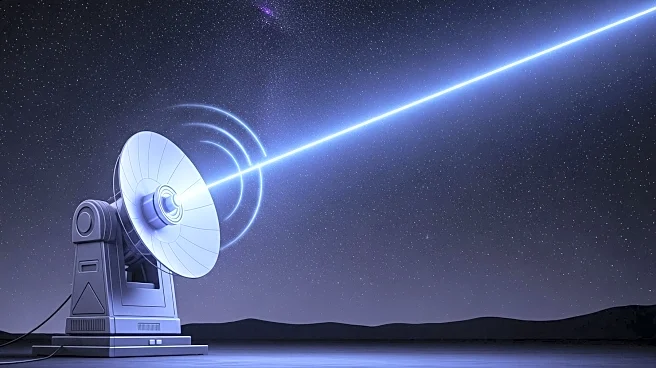
Cailabs, a France-based company, has launched the Tilba-L10 laser ground station, which aims to revolutionize satellite communication by moving away from traditional radio waves. The optical technology used in Tilba-L10 is less susceptible to weather disruptions and is more secure against detection and jamming by hostile entities. This system can transmit data at speeds up to 20 gigabits per second, significantly surpassing the 1 to 2 gigabits per second typically achieved by radio waves. Since its launch in November 2024, the Tilba-L10 has attracted buyers from several countries, including Australia, France, and the United States.
Why It's Important?
The introduction of the Tilba-L10 laser ground station represents a significant advancement in satellite communication technology. By offering higher data transmission speeds and improved security, this technology could enhance various sectors reliant on satellite data, such as telecommunications, defense, and space exploration. The ability to transmit data more efficiently and securely could lead to improved global connectivity and bolster national security measures. Countries investing in this technology may gain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving field of satellite communications.
What's Next?
As Cailabs continues to expand its market reach, further adoption of the Tilba-L10 technology is expected. This could lead to increased collaboration with international space agencies and private companies seeking to enhance their satellite communication capabilities. The ongoing development and refinement of optical communication technologies may also spur innovation in related fields, potentially leading to new applications and services.
Beyond the Headlines
The shift from radio to optical communication in satellites could have long-term implications for global communication infrastructure. As more entities adopt this technology, there may be a need to update regulatory frameworks and international agreements governing satellite communications. Additionally, the increased security offered by optical technology could influence geopolitical dynamics, as nations seek to protect their data transmission capabilities from potential adversaries.