Excess Protein Concerns
The human body has specific protein requirements, which vary based on activity levels, overall health, and individual physiology. While protein is essential
for muscle repair, hormone production, and overall bodily function, excessive consumption can lead to adverse effects. One of the main things to look out for is changes in your digestive system. Eating too much protein may strain the kidneys as they work harder to filter waste products of protein metabolism. Another area of concern is how protein intake may impact other food groups and lead to insufficient consumption of other important nutrients. Understanding these potential risks helps individuals make informed decisions about their protein consumption, promoting long-term health and well-being. It's always wise to focus on eating a well-rounded diet.
Digestive Distress Signals
One clear sign that you may be overeating protein is trouble with digestion. High protein intake can often result in issues like bloating, constipation, and increased gas. These issues may arise because the body struggles to process and eliminate the byproducts of excessive protein metabolism. The digestive system may get overwhelmed if it cannot cope with the increased burden of processing large quantities of protein. These symptoms can cause discomfort and can point to an imbalance in your diet. If you experience these digestive issues after consuming protein-rich meals, it might be time to evaluate and adjust your protein intake. The body’s signals are important, and listening to these signals will help in making healthy lifestyle choices.
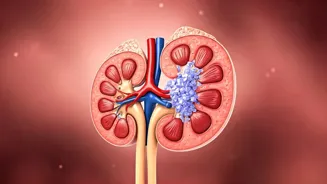
Kidney Strain Warnings
Your kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste products from the blood, including those generated by protein metabolism. Consuming an excessive amount of protein can put added pressure on these important organs. As the kidneys work harder, they may become overworked, potentially leading to long-term health problems. If you have pre-existing kidney issues or a family history of kidney disease, it is especially important to be careful about your protein intake. Symptoms to watch out for include frequent urination and increased thirst. Monitoring these warning signs will help to ensure you stay healthy and well-hydrated. If you are concerned about your kidney health, it's best to talk to your doctor to get personalized dietary recommendations.
Dietary Imbalance Concerns
A diet that is excessively high in protein sometimes lacks variety. When you consume too much protein, it can sometimes displace other essential nutrients. This often means you may be eating fewer carbohydrates, fats, or fiber-rich foods. A balanced diet is critical for optimal health. Each macronutrient has its role, and neglecting any of them can cause imbalances. Insufficient fiber intake can lead to digestive problems. Likewise, inadequate intake of carbohydrates can impact your energy levels and overall metabolic health. Regularly assess your diet and prioritize a variety of nutritious foods. This approach will help you meet all your nutritional needs.
Excess Protein Assessment
How much protein is considered too much? The optimal protein intake varies based on individual needs and activity levels. While general recommendations suggest a range of around 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day for sedentary individuals, active people may need more. Consuming significantly higher amounts than this, without proper guidance, may increase the risk of the previously mentioned health problems. Assessing your current protein intake requires understanding the protein content of the foods you eat. The easiest way to do this is to track your daily food consumption, calculate your total protein intake, and compare it to the recommended daily values. A dietitian or a healthcare professional can provide individualized guidance based on your specific needs and health profile.