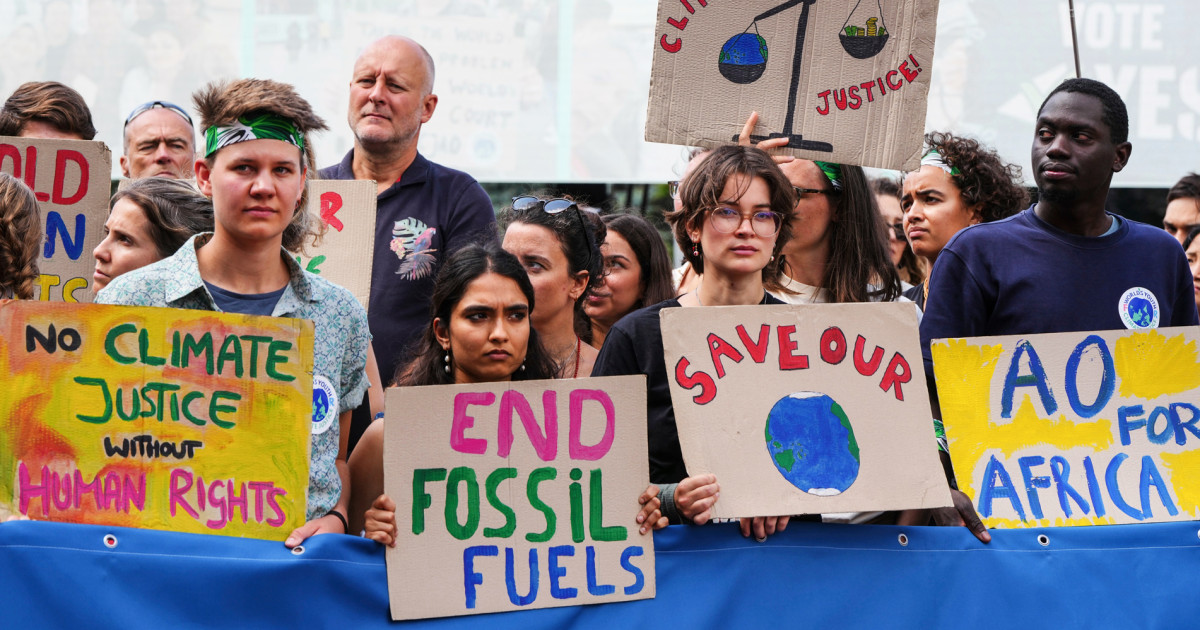The International Court of Justice has taken a historic step in the fight against climate change, issuing an advisory opinion that underscores the urgent need for nations to take immediate action. Declaring
Did You Know
The shortest war lasted 38 minutes.
?
AD
climate change an "urgent and existential threat," the court established that countries failing to address this crisis may be in violation of international law. This landmark ruling opens the door for affected nations to seek reparations for damages caused by climate impacts, marking a pivotal moment in the evolution of international climate law.
With the ruling, the ICJ has reinforced the idea that environmental protection is a fundamental human right that nations must uphold. Judges, including Judge Yuji Iwasawa, emphasized that existing international treaties impose obligations on countries to mitigate emissions and cooperate in addressing climate change. This decision gives environmental advocates a significant legal framework through which they can mobilize support and hold both countries and corporate polluters accountable for their roles in exacerbating climate crises.
The tiny island nation of Vanuatu, heavily impacted by rising sea levels and climate-related disasters, played a central role in advocating for the ICJ to clarify these legal obligations. Their efforts highlight the vital need for global solidarity in combating climate change, particularly for vulnerable populations at risk of losing their homes. As the court's opinion echoes around the world, it serves as a call to action, urging every nation to cooperate in the fight against climate change and to take meaningful steps to protect the planet for generations to come.
Q&A (Auto-generated by AI)
What is the ICJ's role in climate law?
The International Court of Justice (ICJ) serves as the principal judicial body of the United Nations, resolving disputes between states and providing advisory opinions on international legal issues. In the context of climate law, the ICJ's recent advisory opinion emphasizes that countries have legal obligations to combat climate change and protect the environment. This opinion is significant as it establishes a legal framework for nations to be held accountable for their actions or inactions regarding climate change.
How does climate change impact international law?
Climate change poses unique challenges to international law by raising questions about state responsibilities and obligations. The ICJ's recent ruling indicates that nations could be in violation of international law if they fail to address climate change effectively. This ruling aligns with growing recognition that climate protection is a human right, compelling states to take proactive measures against environmental degradation and to consider the legal ramifications of their actions.
What are the implications of the ICJ ruling?
The ICJ's ruling has far-reaching implications for international climate policy. It establishes that countries must cooperate to mitigate climate change and could face legal consequences for failing to do so. This advisory opinion may pave the way for future litigation against states and corporations that contribute to climate harm, potentially leading to reparations for affected nations. It also emphasizes the need for stronger international treaties and commitments to combat climate change.
What legal obligations do countries have for climate?
Countries are legally obligated to take measures to mitigate climate change under international treaties like the Paris Agreement. The ICJ's recent opinion reinforces these obligations by stating that nations must protect both current and future generations from environmental harm. This includes reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to the impacts of climate change, thereby holding states accountable for their contributions to global warming.
How might this ruling affect future lawsuits?
The ICJ's ruling could significantly impact future lawsuits related to climate change by providing a legal precedent for holding states accountable for inaction. Environmental groups and affected nations may use this advisory opinion to pursue legal action against governments and corporations that fail to meet their climate obligations. It may also encourage the development of new legal frameworks and strategies for climate litigation, broadening the scope of accountability in environmental law.